




Next: Fourier analysis and resynthesis
Up: Filters
Previous: Making and using all-pass
Contents
Index
- A recirculating elementary filter has a pole at
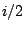 . At what angular
frequency is its gain greatest, and what is the gain there? At what angular
frequency is the gain least, and what is the gain there?
. At what angular
frequency is its gain greatest, and what is the gain there? At what angular
frequency is the gain least, and what is the gain there?
- A shelving filter has a pole at 0.9 and a zero at 0.8. What are: the DC
gain; the gain at Nyquist; the approximate transition frequency?
- Suppose a complex recirculating filter has a pole at
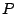 . Suppose
further that you want to combine its real and imaginary output to make a
single, real-valued signal equivalent to a two-pole filter with poles at
. Suppose
further that you want to combine its real and imaginary output to make a
single, real-valued signal equivalent to a two-pole filter with poles at 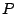 and
and 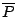 . How would you weight the two outputs?
. How would you weight the two outputs?
Miller Puckette
2006-09-24