




Next: Automation and voice management
Up: Audio and control computations
Previous: MIDI-style synthesizer
Contents
Index
- How many partials of a tone at A 440 can be represented digitally at a
sample rate of 44100 Hertz?
- What frequency would you hear if you synthesized a sine wave at 88000 Hertz
at a sample rate of 44100?
- Suppose you are synthesizing sound at 44100 Hertz, and are computing
64-sample audio blocks. A control event is scheduled to happen at an elapsed
time of exactly one second, using the fast-as-possible update scheme. At what
sample does the update actually occur?
- Sampling at 44100, we wish to approximately play a tone at middle C by
repeating a fixed waveform every N samples. What value of
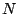 should we
choose, and how many cents (Page
should we
choose, and how many cents (Page ![[*]](file:/usr/local/share/lib/latex2html/icons/crossref.png) ) are we off from the
``true" middle C?
) are we off from the
``true" middle C?
- Two sawtooth waves, of unit amplitude, have frequencies 200 and 300 Hertz,
respectively. What is the periodicity of the sum of the two? What if you
then wrapped the sum back to the range from 0 to 1? Does this result change
depending on the relative phase of the two?
- Two sawtooth waves, of equal frequency and amplitude and one half cycle
out of phase, are summed. What is the waveform of the sum, and what are its
amplitude and frequency?
- What is the relative level, in decibels, of a sawtooth wave's third
harmonic (three times the fundamental) compared to that of the fundamental?
- Suppose you synthesize a 44000-Hertz sawtooth wave at a sample rate
of 44100 Hertz. What is the resulting waveform?
- Using the techniques of Section 3.7, draw a block diagram
for generating two phase-locked sinusoids at 500 and 700 Hertz.
- Draw a block diagram showing how to use thresholding to detect when one
audio signal exceeds another one in value. (You might want to do this to
detect and filter out feedback from speakers to microphones.)





Next: Automation and voice management
Up: Audio and control computations
Previous: MIDI-style synthesizer
Contents
Index
Miller Puckette
2006-09-24