




Next: Designer spectra
Up: Modulation
Previous: Phase modulation and FM
Contents
Index
- A sound has fundamental 440. How could it be ring modulated to
give a tone at 110 Hz with only odd partials? How could you then fill in the
even ones if you wanted to?
- What carrier and modulation frequencies would you give a two-operator FM
instrument to give frequencies of 618, 1000, and 2618 Hz? (This is
a prominent feature of Chowning's Stria [DJ85].)
- Suppose you wanted to make FM yet more complicated by modulating the
modulating oscillator, as in:
How would the spectrum differ from that of the simple two-modulator example
(section 5.5.7)?
- A sinusoid at a frequency
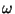 is ring modulated by another
sinusoid at exactly the same frequency. At what phase differences will the
DC component of the result disappear?
is ring modulated by another
sinusoid at exactly the same frequency. At what phase differences will the
DC component of the result disappear?
msp
2003-12-08