




Next: Wavetables and samplers
Up: Sinusoids, amplitude and frequency
Previous: More additive synthesis
Contents
Index
- If 0 dB corresponds to an amplitude of 1,
how many dB corresponds to amplitudes of 1.5, 2, 3, and 5? (Answer:
about 3, 6, 10, and 14.)
- Two uncorrelated signals of RMS amplitude 3 and 4 are added; what's the
RMS amplitude of the sum?
- How many uncorrelated signals, all of equal amplitude, would you have
to add to get a signal that is 9 dB hotter?
- What is the angular frequency of middle C at 44100 samples per second?
- If an audio signal
![$x[n], n = 0, ..., M-1$](img155.png) has peak amplitude 1, what
is the minimum possible RMS amplitude? What is the maximum possible?
has peak amplitude 1, what
is the minimum possible RMS amplitude? What is the maximum possible?
- If
![$x[n]$](img78.png) is the Sinusoid of Section 1.1, and making the assumptions
of section 1.2, show that its RMS amplitude is approximately
is the Sinusoid of Section 1.1, and making the assumptions
of section 1.2, show that its RMS amplitude is approximately 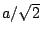 .
Hint: use an integral to approximate the sum. Since the window contains
many periods, you can assume that the integral covers a whole number of periods.
.
Hint: use an integral to approximate the sum. Since the window contains
many periods, you can assume that the integral covers a whole number of periods.
Miller Puckette
2006-03-03